TAMPA BAY rEGENERATIVE MEDICINE
Mesenchymal Stem Cell Therapy
What is Regenerative Medicine?
Regenerative Medicine is a form of molecular biology and tissue engineering that is used to restore natural function to damaged tissues and organs.
What are Mesenchymal Stem Cells (MSCs)?
MSCs are multipotent, undifferentiated stem cells, which means they have the capacity to self-renew and the ability to develop into multiple specialized cell types present in a specific tissue or organ.
MSCs are commonly collected from the patient’s own bone marrow or adipose (fat) tissue and then injected into the area of concern. At our office, however, we utilize donor birth tissue to obtain MSCs, as this is when MSCs are most potent.
Who Can Benefit from Regenerative Medicine?
Individuals suffering from any of the following conditions may be a candidate for Regenerative Medicine:
- Joint Pain
- Osteoarthritis
- Sports Injuries
- Recommended for Certain Surgeries
The majority of our patients come to us seeking Regenerative Medicine as an alternative to surgery or heavy medication.
Why not Surgery?
Regenerative Medicine with the use of MSCs is an alternative option to more invasive procedures such as surgery, as the problem area is directly targeted with the injections. Benefits to receiving MSC therapy over surgery include the relative ease of the procedure and reduced recovery time. Generally, MSC therapy patients comfortably walk out on their own, and can typically return to daily routines within a few days.
What are the risks of surgery?
While surgery may be the right path for some, for others it comes with high risk, painful recovery, and unguaranteed results.
The risks involved in a surgical procedure are sometimes difficult to predict and prevent. These can include infection and blood clots.
- Infection can occur at any time, whether it is during the procedure itself, after the patient’s return home, or months down the line after the patient assumed themselves healed. The more time that passes between the procedure and the infection, the more difficult it is to heal. Treating an infection can be very invasive and can range from intravenous antibiotics to an additional surgical procedure to remove the infection.
- Blood clots occur when blood binds to itself and thickens, which results in decreased blood flow. Blood clots often form after a surgical procedure when the patient has decreased mobility and therefore slowed the movement of the blood in their veins. Clots can also form during long surgical procedures, as blood stills and pools while the patient is on the operating table.
Are MSCs Safe?
There are many advantages of using Mesenchymal Stem Cells from umbilical cord birth tissue, as opposed to MSCs from bone marrow or adipose tissue.
- Since our MSCs are donated, the procedure is minimally invasive and very low-risk. When collecting MSCs from bone marrow or adipose tissue, there’s always a risk of possible infection as these procedures are more invasive.
- Our less invasive procedure reduces risk as we are specifically targeting the area of concern with the MSC injections.
- Umbilical cord MSCs are epigenetically young due to their source. This means that the quality of stem cell is better because the earlier MSCs are collected, the more active they are. The quality of MSCs and their effectiveness decreases with age.
Our regenerative tissue is obtained from expectant mothers that have completed a series of comprehensive panel tests and whose pregnancies have been deemed normal.
Once the umbilical cord tissue has been donated, it is transported to the processing facility where pre-screening takes place. The MSCs are carefully handled and preserved to protect cell viability. All tissues are retested again after pre-screening to ensure the absence of any foreign pathogens.
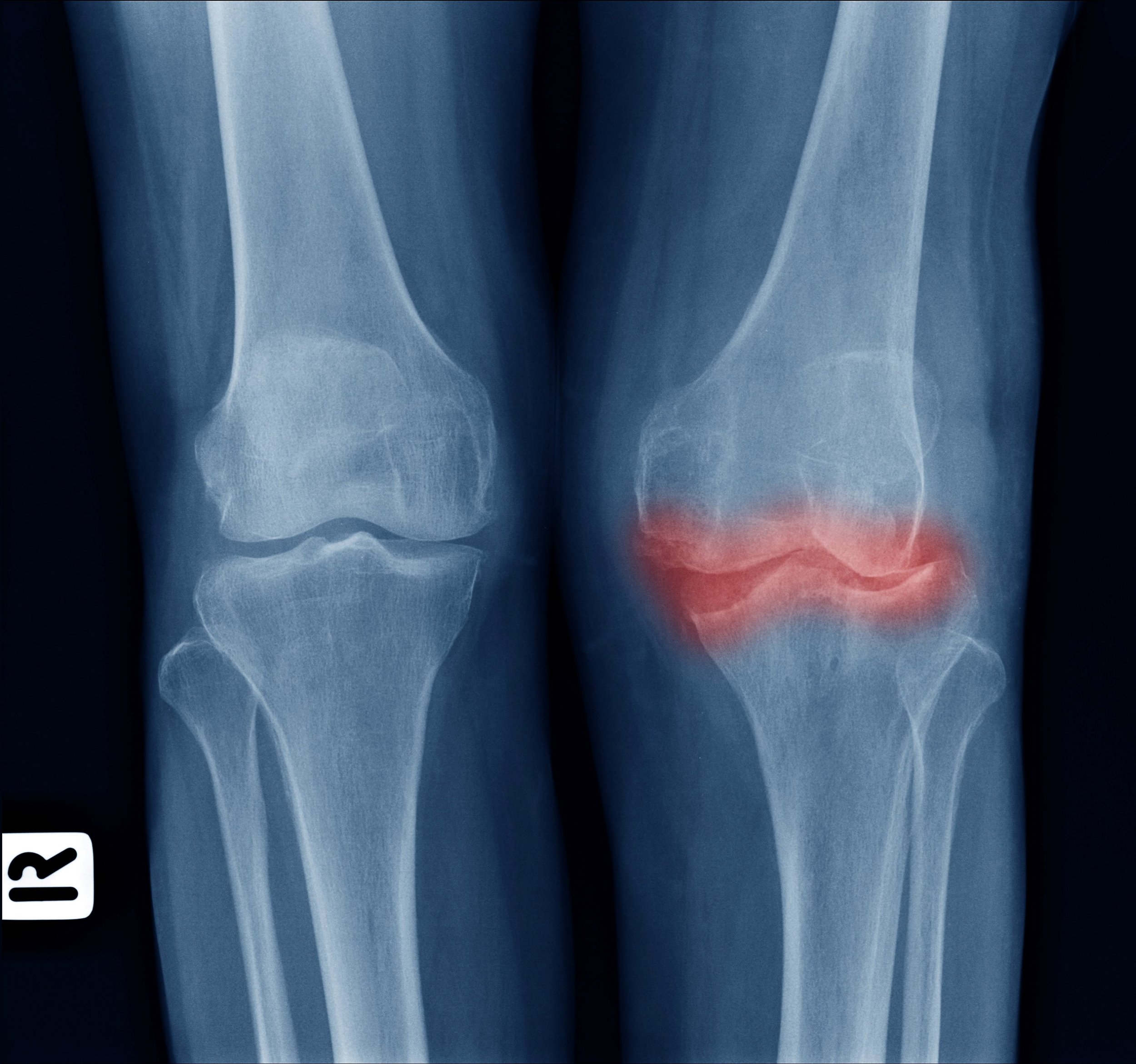
Knee Before Stem Cell
Knee After Stem Cell